IoT the term refers to the connection of devices (the Things) through the internet so they can collect and share data without human assistance.
The adoption of IoT within the industry has opened up unlimitted possibilities and are rapidly redefining all areas of business operations. Pioneering companies are connecting complex physical machinery with data analytics, bringing unforeseen insights, increasing efficiency and opening up a new era of competitiveness and growth.
The Industrial Revolution was the transition to new manufacturing processes in the period from about 1760 to sometime between 1820 and 1840. This transition included going from hand production methods to machines, new chemical manufacturing and iron production processes, the increasing use of steam power, the development of machine tools and the rise of the factory system.
First industrial revolution was the transition to new manufacturing process in the period of 1760 to 1840. This is the transition from hand production methods to machines.Important developments are textile industry powered by steam, efficiency of steam engine is increased & used in rotary motions ,Iron making.This is characterized by the dominance of the textile industry and the use of coal. The symbols are the steam engine and train.
The 2nd industrial revolution is marked by a wide range of sectors entirely new as the chemical industry, mechanical engineering. If the energy in the 1st industrial revolution was coal in the 2nd industrial revolution were the oil and electricity.The results of science flow in areas especially in the chemical industry that made great changes in the pharmaceutical and food industries. The symbol of the 2nd industrial revolution is steel.
The 3rd industrial revolution in the 20th century has changed Manufacturing a lot. New technologies, such as the Internet, and the renewable energies changed the history.Products are produced in a new way, using computers and new machines
Industry 4.0 or fourth industrial revolution is inspired by German government's initiative to promote connected manufacturing industry , business & other related process. The vision of I4.0 is is for smart factory & make use of digital transformation.The Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) is driving the fourth wave of the industrial revolution.
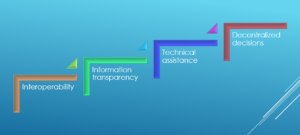
The four design principles in Industry 4.0 are below & these principles support companies in implementing smart factory industry 4.0:
- Interoperability : The ability of machines, devices, sensors, and people to connect and communicate with each other via the Internet of Things (IoT)
- Information transparency: Aggregation of raw sensor data to higher-value context information
- Technical assistance: The ability of assistance systems to solve urgent problems on short notice by aggregating and visualizing information comprehensively.
- Decentralized decisions:The ability of cyber physical systems to make decisions on their own and to perform their tasks as autonomously as possible..
IIoT definition:
Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) refers to the use of Internet of Things (IoT) technologies in manufacturing and related industries like agriculture, gas and oil, utilities, and transportation to create smart, self-regulating systems.The Industrial Internet of Things is opening up a new era of economic growth and competitiveness, this will transform companies and countries. We are looking at a future where the intersection of people, data and intelligent machines will have high reaching impacts on the productivity, efficiency and operations of industries around the world.
The basic idea is to give the machines the main power in our economy to make it “smarter” by gathering and analyzing data, often in real-time, and taking appropriate actions on the go.These machines can also identify when they need maintenance and perform self-maintenance. This has the effect of preventing breakdowns and reduce the downtime, increasing the overall production capacity and throughput.
Gartner is assuming 60% of IIoT analytics will be on-premise so this appears to drive the on-premise requirement. On-premise is certainly going to be important but 60% seems very high. It will be interesting to see if this continues to be a criterion since Gartner has left out some of the key leaders in the industry 4.0 companies.
The top industries adopting IoT are not a big surprise, the top 3 being: Industrial Products, Electronics and High Tech, and Automotive. Why Insustrial IoT , the answer is For any business that deals with the production and/or transportation of physical goods, IIoT can create game-changing operational efficiencies and present entirely new business models.
The major driver of industry 4.0 or we can say manufacturing 4.0 are
- Wide spread use of sensors in Industrial IoT
- Data analytics ( Bigdata)
- Artificial intelligence & machine learning
- Augmented reality systems
- Touch & voice interfaces
- Robotics
Benefits of IIOT:
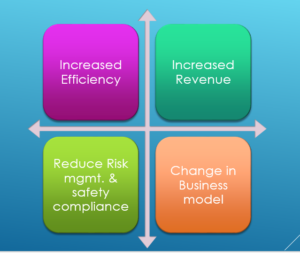
we believe the IIoT provides benefits across four key areas,
- Increased Efficiency: Capturing of more data about their processes and products through the use of technologies such as sensors and the data collected will provide valuable information to transform business practices or make real-time decisions.
- Increased Revenue: IIOT opens up new models of business and brings new sources of revenue. The IIoT can help to monetize additional services on top of existing products.
- Change in Business Models: The IIoT allows automation of some processes that can improve time-to-market, measure performance and rapidly respond to customer needs.New services and products are emerging & enabling new approaches create great value for customers.
- Reduce Risk Management and Safety Compliance : IIoT can help reduce risk and monitor safety protocol adherence by identifying the areas where Machines can learn to monitor and audit compliance procedures, flagging irregularities and issues much more quickly than humans can.
Challenges in implementation of Industry 4.0:
- IT security issues
- Reliability and stability needed for critical machine-to-machine communication
- Need to maintain the integrity of production processes
- Protect industrial know how
- Lack of adequate skill-sets
- Threat of redundancy of the corporate IT department
- General reluctance to change by stakeholders
- Loss of jobs due to automation
- Low top management commitment
- Unclear legal issues and data security
- Unclear economic benefits/ Excessive investment
- Lack of regulation, standard and forms of certifications